7. Troubleshooting
1. Template Not Found
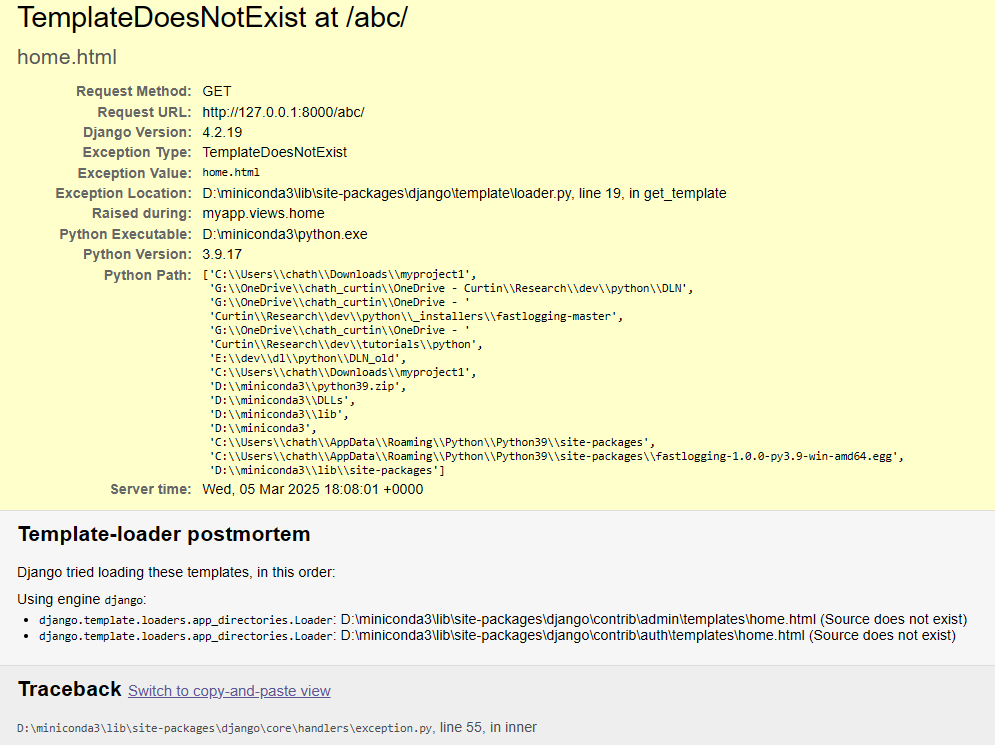
Solution:
Django is unable to find the html file in the app since the app is not registered in INSTALLED_APPS in settings.py
2. Admin Frontend Breaks when DEBUG=False
Django Admin CSS when you turn of the Debug Mode (Debug = False) does not automatically serve static files in production mode. One way to deal with is to manually server the files. You can follow the steps below to do it:
Step 1: Ensure STATIC_ROOT is Set in settings.py
First, verify that your settings.py file includes the correct configuration for static files:
import os
# Static files settingsSTATIC_ROOT = os.path.join(BASE_DIR, 'staticfiles')This ensures that all static files, including those for the Django admin panel, are collected in one location.
Step 2: Manually Create the staticfiles Directory
Before running the collectstatic command, manually create the staticfiles directory in your project root (where manage.py is located).
# On Windows (Command Prompt or PowerShell):mkdir staticfiles
# On macOS/Linux (Terminal):mkdir staticfilesThis step ensures that Django has a valid destination to store the collected static files.
Step 3: Run collectstatic to Gather Static Files
Now, run the following command in your terminal to collect all static files into the STATIC_ROOT directory:
python manage.py collectstatic --noinputYou should see output similar to:
127 static files copied to 'C:\path\to\your\project\staticfiles'.If you encounter an error stating "You're using the staticfiles app without having set the STATIC_ROOT", make sure you have correctly defined STATIC_ROOT as shown in Step 1.
Step 4: Temporarily Serve Static Files in Development
Since Django does not serve static files when DEBUG=False, you need to configure it manually.
Modify urls.py to allow Django to serve static files while testing locally:
from django.urls import re_pathfrom django.views.static import servefrom django.conf import settings
if settings.DEBUG is False: urlpatterns += [re_path(r'^static/(?P<path>.*)$', serve,{'document_root': settings.STATIC_ROOT})]Step 5: Restart Django Server
After completing the above steps, restart your Django development server:
python manage.py runserverNow, when you access the Django admin panel, the static files (CSS, JavaScript) should load correctly, even with DEBUG=False.
2.1 Alternative Solution
python manage.py runserver --insecureis used to start the development server while serving static files, even when DEBUG = False in the settings.
Implications of Using --insecure
-
Serving Static Files in Production-Like Settings
- Normally, Django does not serve static files when
DEBUG = Falsebecause static files should be handled by a production-ready web server like Nginx or Apache. - The
--insecureflag forces Django to serve static files directly, even withDEBUG = False.
- Normally, Django does not serve static files when
-
Security Risks
- Using
--insecurein a production environment is not recommended, as Django’s development server is not optimized or secure for handling production traffic. - This flag bypasses Django’s default behavior of refusing to serve static files in non-debug mode, which can expose sensitive files if improperly configured.
- Using
-
When to Use It?
- It is useful for quick testing in a staging or development environment where
DEBUG = False, but you don’t have a proper static file server set up yet. - It should never be used in production.
- It is useful for quick testing in a staging or development environment where

